The anterior horn sends out motor signals to the skeletal muscles. The posterior grey column of the spinal cord is one of the three grey columns of the spinal cord.

The Gray Matter Makes Up The Core Of The Spinal Cord In A Butterfly Like Shape It Consists Of Two Posterior Dorsal Horns Tw Spinal Cord Spinal Spinal Nerve
What is a posterior horn cell.
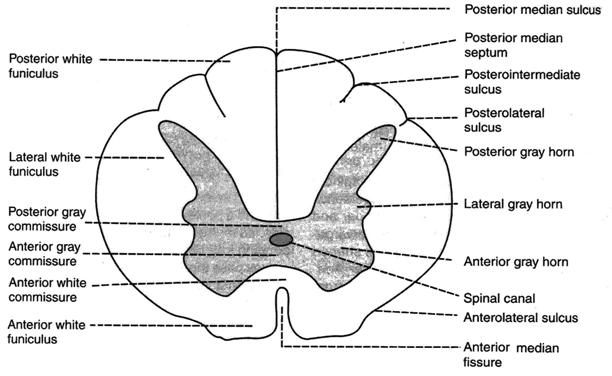
. The nuclei of the posterior horn are the marginal nucleus TA nucleus marginalis TA gelatinous substance TA substantia gelatinosa TA nucleus proprius TA secondary visceral grey substance TA. The posterior horn or gray column of the spinal cord as appearing in cross section. Gray Horns The posterior horn is responsible for sensory processing.
The lateral horn which is only found in the thoracic upper lumbar and sacral regions is the central component of the sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system. In transverse sections the gray matter is conventionally divided into dorsal posterior lateral and ventral anterior horns The neurons of the dorsal horns receive sensory information that enters the spinal cord via the dorsal roots of the spinal nerves. A longitudinal subdivision of gray matter in the dorsal part of each lateral half of the spinal cord that receives terminals from some afferent fibers of the dorsal roots of the spinal nerves.
It contains the substantia gelatinosa. It contains the substantia gelatinosa. The anterior horn sends out motor signals to the skeletal muscles.
In the dorsal horns or posterior horns many incoming sensory neurons synapse with interneurons which then distribute information to other parts of the spinal cord and brain. It receives several types of sensory information from the body including fine touch proprioception and vibration. The anterior grey column is the column where the cell bodies of alpha motor neurons are located.
The dorsal horn functions as an intermediary processing center for this information comprising a complex network of excitatory and inhibitory interneurons as well as projection neurons which transmit the processed somatosensory information from the spinal cord to the brain. Called also dorsal column. The posterior horn posterior cornu dorsal horn spinal dorsal horn of the spinal cord is the dorsal more towards the back grey matter of the spinal cord.
Other articles where dorsal horn is discussed. In cross-sections the spinal cord consists of a central butterfly-shaped zone of gray matter and an outer rim of white matter. The posterior horn TA or dorsal horn TAalt contains spinal laminae I-VI TA of Rexed.
The anterior grey column contains motor neurons that affect the skeletal muscles while the posterior grey column receives information regarding touch and sensation. The ventral horn also known as the. The anterior grey column is the front column of grey matter in the spinal cord.
The lateral horn which is only found in the thoracic upper lumbar and sacral regions is the central component of the sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system. One of the divisions of the grey matter of the spinal cord the posterior horn contains interneurons that make connections within the spinal cord as well as neurons that enter ascending sensory pathways. The posterior grey column posterior cornu dorsal horn spinal dorsal horn posterior horn sensory horn of the spinal cord is one of the three grey columns of the spinal cord.
What is the dorsal column medial lemniscus pathway. The posterior horn is responsible for sensory processing. Nervethe posterior gray column dorsal horn of the cord or ascend to nuclei in the lower part of the brain.
Within the spinal dorsal horn however the different. The dorsal horn also known as the posterior horn contains neurons that receive somatosensory information from the body which is then transmitted via the ascending pathways to the brain. The posterior grey column posterior cornu dorsal horn spinal dorsal horn posterior horn sensory horn of the spinal cord is one of the three grey columns of the spinal cord.
The grey matter forms the core of the spinal cord and. Posterior part of gray matter Function. The grey matter is made up predominantly of neurons specialized nerve cells which transfer messages to other nerve cells and glial cells which surround and insulate the neuron cells.
The dorsal posterior horn neurons receive incoming afferent sensory signals while the ventral anterior horn neurons. The grey matter is divided into four main columns. It receives several types of sensory information from the body.
The posterior gray horn contain cell bodies and axons of interneurons as well as axons of sensory neurons. The spinal dorsal horn is regarded as a unit that executes the function of sensory information processing without any significant communication with other regions of the spinal gray matter. The branches of this trunk distribute both.
One of the divisions of the grey matter of the spinal cord the posterior horn contains interneurons that make connections within the spinal cord as well as neurons that enter ascending sensory pathways. As shown in Figure 1441 the gray matter is subdivided into regions that are referred to as horns. The anterior horn sends out motor signals to the skeletal muscles.
The gray matter is the area of the spinal cord where many types of neurons synapse. The lateral gray horn is present only in thoracic and upper lumbar segments of the spinal cord and contain autonomic motor nuclei. This information is sent from receptors of the skin bones and joints through sensory neurons whose cell bodies lie in the dorsal root ganglion.
Immediately lateral to the spinal ganglia the two roots unite into a common nerve trunk which includes both sensory and motor fibres. Posterior horn of the spinal cord. It is one of the three grey columns.
Gray Horns The posterior horn is responsible for sensory processing. Posterior gray horn Contains neuron cell bodies that recieve impulses from sensory neurons Gray Commissure Narrow bridge of gray matter that connects the right and left sides of gray matter. It receives several types of sensory information from the body including fine touch proprioception and vibration.
Sensory nuclei- somatic and visceral -receives information from skeletal muscles and skin somatic and visceral organs visceral and relays it to CNS. Spinal Cord Internal Structure- Gray matter. Spinal Cord Gray Matter Functions.
It receives several types of sensory information from the body including light touch proprioception and vibration. Reflex actions The spinal cord is an integrating centre for most reflexes. The dorsal horn the intermediate column the lateral horn and the ventral horn.
Medical Definition of dorsal horn.

Neurons In Anterior Gray Horn Studopediya Net
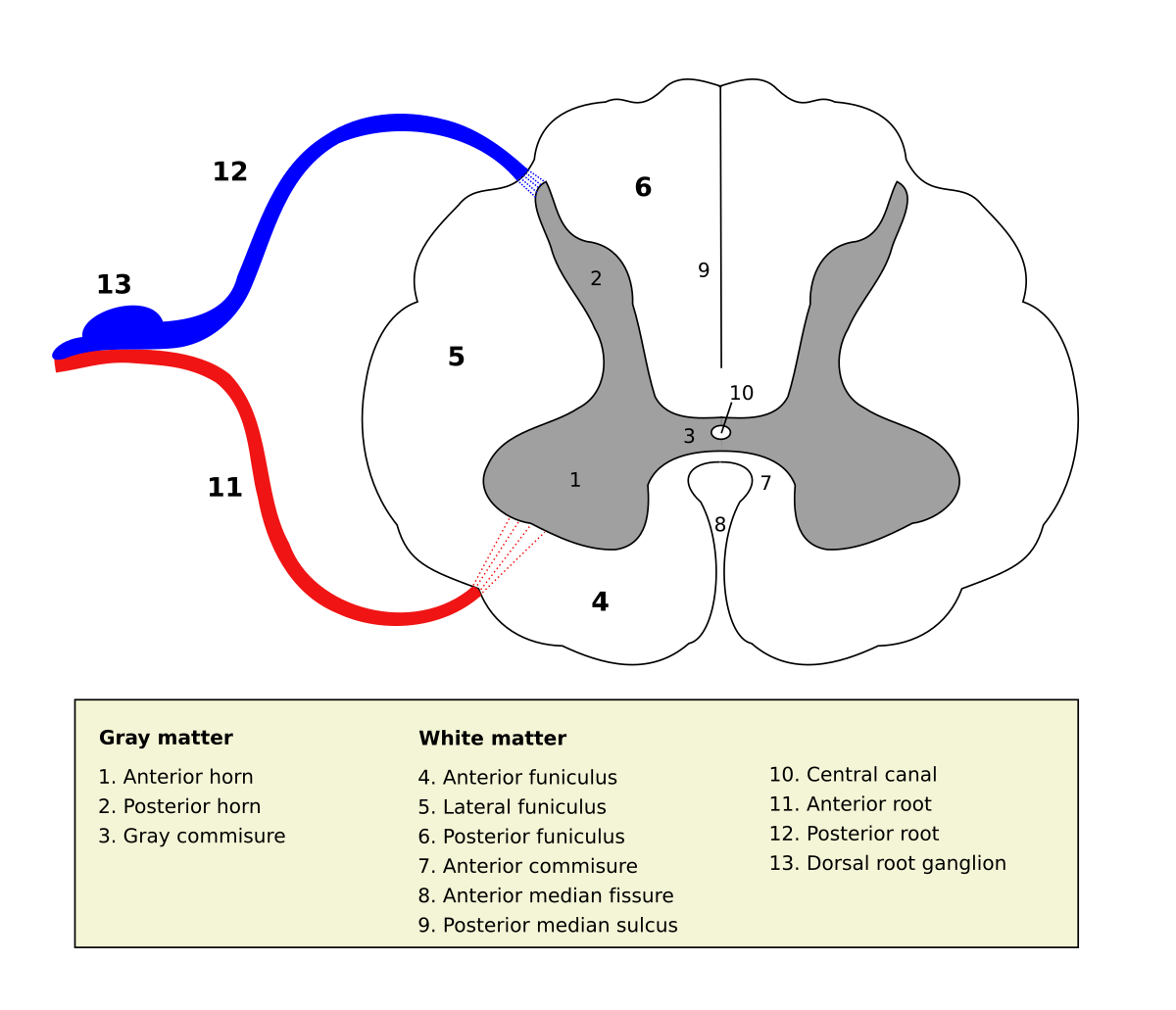
Posterior Grey Column Wikipedia
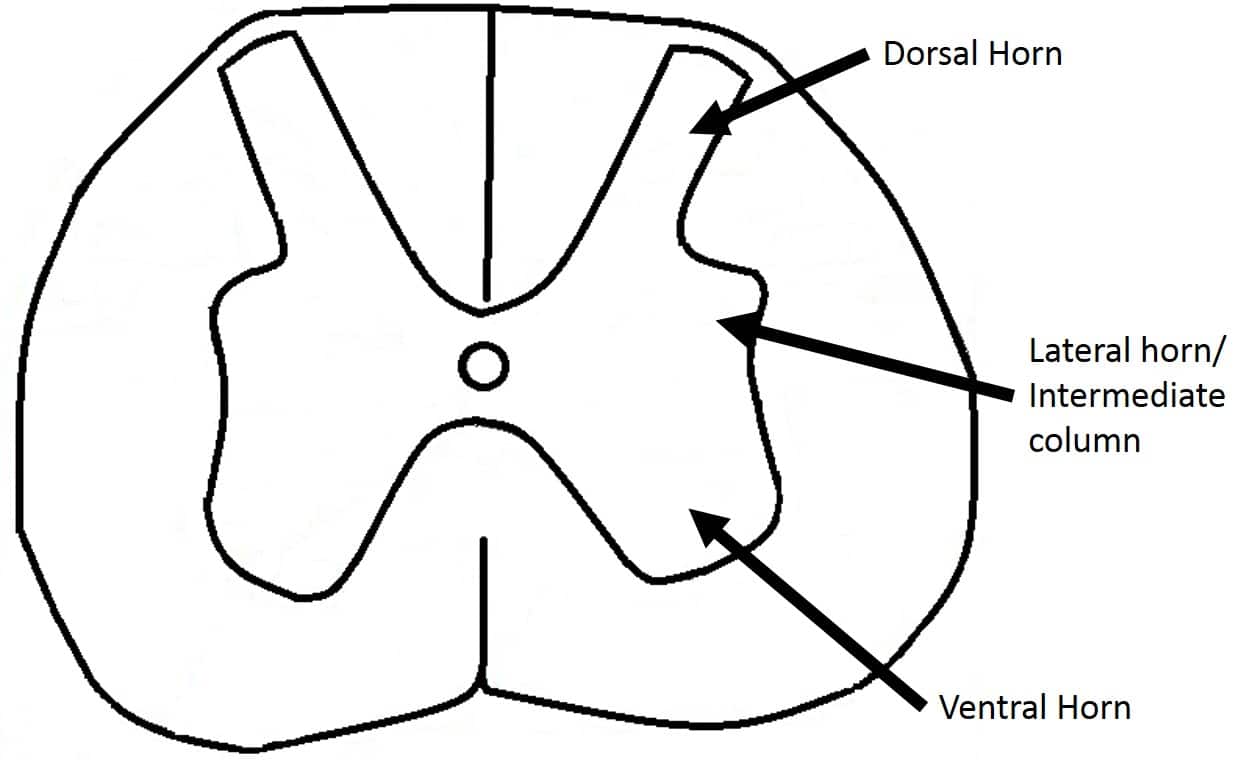
The Grey Matter Of The Spinal Cord Teachmeanatomy

Dorsal Horn Anatomy Britannica
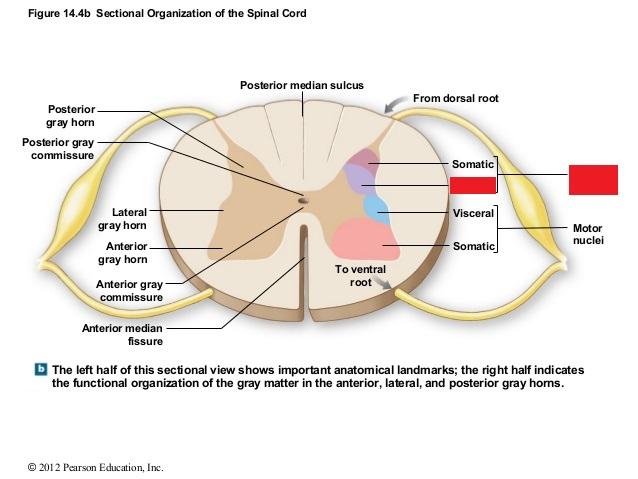


0 comments
Post a Comment